Publications
2026
- AI
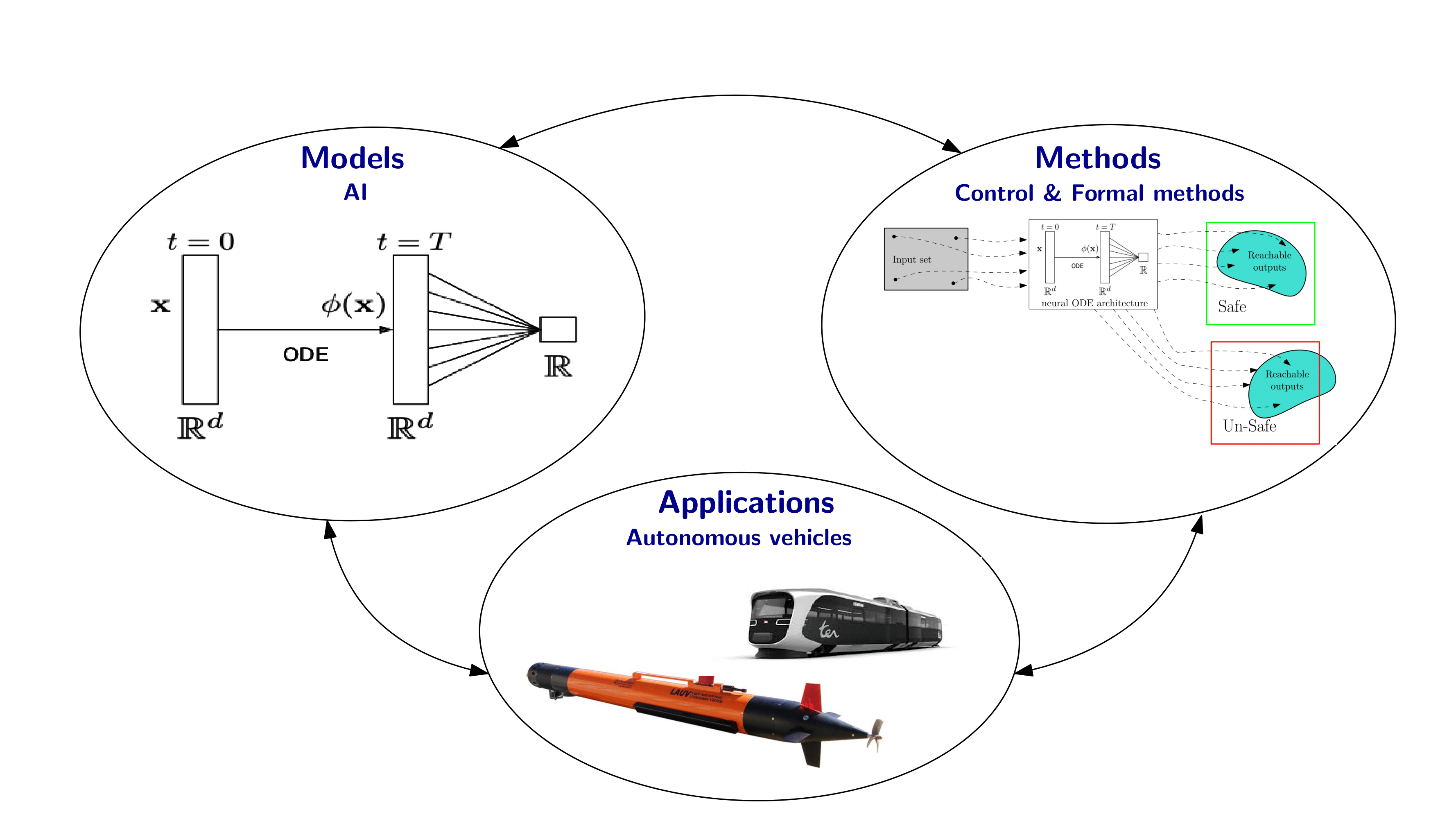 Formal Verification of Neural ODE for Safety Evaluation in Autonomous VehiclesAbdelrahman Sayed SayedIn AAAI-26 Doctoral Consortium, 2026
Formal Verification of Neural ODE for Safety Evaluation in Autonomous VehiclesAbdelrahman Sayed SayedIn AAAI-26 Doctoral Consortium, 2026Higher autonomy is an increasingly common goal in the design of transportation systems for the cities of the future. Recently, part of this autonomy in both rail and maritime transport has come from the field of artificial intelligence and machine learning, particularly for perception tasks (detection and recognition of rail signals, other vessels, or other elements in the vehicle environment) using neural networks. Although AI-based approaches have gained significant popularity in many application fields due to their good performance, their unpredictability and lack of formal guarantees regarding their desired behavior present a major issue for the deployment of such safety-critical systems in urban areas. The goal of my PhD thesis is to design new formal methods to analyze and ensure the safety of such AI-based perception modules in autonomous vehicles. More specifically, my PhD topic aims to formally evaluate the safety of a recently introduced class of continuous AI models which are neural ODE.
@inproceedings{sayed2025formal, title = {Formal Verification of Neural ODE for Safety Evaluation in Autonomous Vehicles}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed}, booktitle = {AAAI-26 Doctoral Consortium}, year = {2026}, }
2025
- AI
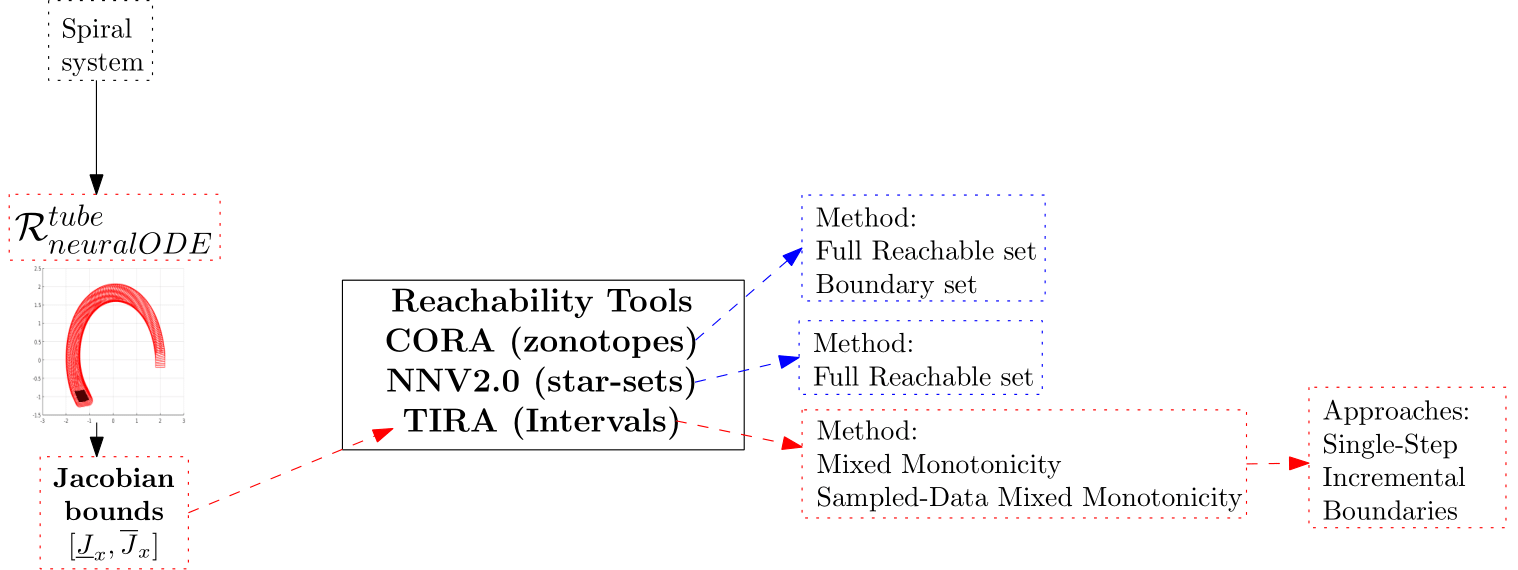 Mixed Monotonicity Reachability Analysis of Neural ODE: A Trade-Off Between Tightness and EfficiencyAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Pierre-Jean Meyer, and Mohamed GhazelIn NeurIPS Workshop on Symmetry and Geometry in Neural Representations, 2025
Mixed Monotonicity Reachability Analysis of Neural ODE: A Trade-Off Between Tightness and EfficiencyAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Pierre-Jean Meyer, and Mohamed GhazelIn NeurIPS Workshop on Symmetry and Geometry in Neural Representations, 2025Neural ordinary differential equations (neural ODE) are powerful continuous-time machine learning models for depicting the behavior of complex dynamical systems, but their verification remains challenging due to limited reachability analysis tools adapted to them. We propose a novel interval-based reachability method that leverages continuous-time mixed monotonicity techniques for dynamical systems to compute an over-approximation for the neural ODE reachable sets. By exploiting the geometric structure of full initial sets and their boundaries via the homeomorphism property, our approach ensures efficient bound propagation. By embedding neural ODE dynamics into a mixed monotone system, our interval-based reachability approach, implemented in TIRA with single-step, incremental, and boundary-based approaches, provides sound and computationally efficient over-approximations compared with CORA’s zonotopes and NNV2.0 star set representations, while trading tightness for efficiency. This trade-off makes our method particularly suited for high-dimensional, real-time, and safety-critical applications. Applying mixed monotonicity to neural ODE reachability analysis paves the way for lightweight formal analysis by leveraging the symmetric structure of monotone embeddings and the geometric simplicity of interval boxes, opening new avenues for scalable verification aligned with the symmetry and geometry of neural representations. This novel approach is illustrated on two numerical examples of a spiral system and a fixed-point attractor system modeled as a neural ODE.
@inproceedings{sayed2025mixedmonotonicityreachabilityanalysis, title = {Mixed Monotonicity Reachability Analysis of Neural ODE: A Trade-Off Between Tightness and Efficiency}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Meyer, Pierre-Jean and Ghazel, Mohamed}, booktitle = {NeurIPS Workshop on Symmetry and Geometry in Neural Representations}, year = {2025}, eprint = {2510.17859}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {eess.SY}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.17859}, } - AI
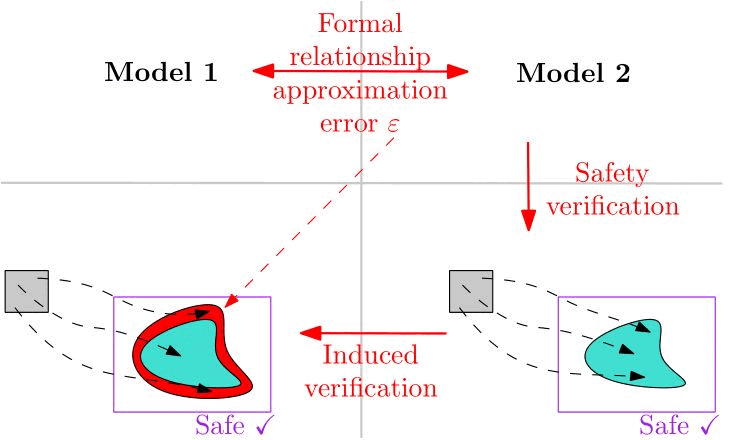 Bridging Neural ODE and ResNet: A Formal Error Bound for Safety VerificationAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Pierre-Jean Meyer, and Mohamed GhazelIn International Symposium on AI Verification, 2025
Bridging Neural ODE and ResNet: A Formal Error Bound for Safety VerificationAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Pierre-Jean Meyer, and Mohamed GhazelIn International Symposium on AI Verification, 2025A neural ordinary differential equation (neural ODE) is a machine learning model that is commonly described as a continuousdepth generalization of a residual network (ResNet) with a single residual block, or conversely, the ResNet can be seen as the Euler discretization of the neural ODE. These two models are therefore strongly related in a way that the behaviors of either model are considered to be an approximation of the behaviors of the other. In this work, we establish a more formal relationship between these two models by bounding the approximation error between two such related models. The obtained error bound then allows us to use one of the models as a verification proxy for the other, without running the verification tools twice: if the reachable output set expanded by the error bound satisfies a safety property on one of the models, this safety property is then guaranteed to be also satisfied on the other model. This feature is fully reversible, and the initial safety verification can be run indifferently on either of the two models. This novel approach is illustrated on a numerical example of a fixed-point attractor system modeled as a neural ODE.
@inproceedings{sayed2025bridgingneuraloderesnet, title = {Bridging Neural ODE and ResNet: A Formal Error Bound for Safety Verification}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Meyer, Pierre-Jean and Ghazel, Mohamed}, booktitle = {International Symposium on AI Verification}, year = {2025}, eprint = {2506.03227}, archiveprefix = {arXiv}, primaryclass = {cs.LG}, url = {https://arxiv.org/abs/2506.03227}, }
2023
- Robotics
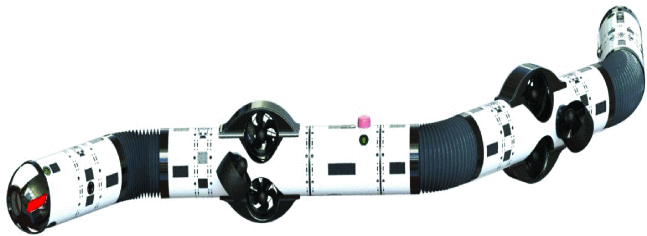 Risk Assessment of an Autonomous Underwater Snake Robot in Confined OperationsAbdelrahman Sayed SayedIn OCEANS 2023-Limerick, 2023
Risk Assessment of an Autonomous Underwater Snake Robot in Confined OperationsAbdelrahman Sayed SayedIn OCEANS 2023-Limerick, 2023The growing interest in ocean discovery imposes a need for inspection and intervention in confined and demanding environments. Eely’s slender shape, in addition to its ability to change its body configurations, makes articulated underwater robots an adequate option for such environments. However, operation of Eely in such environments imposes demanding requirements on the system, as it must deal with uncertain and unstructured environments, extreme environmental conditions, and reduced navigational capabilities. This paper proposes a Bayesian approach to assess the risks of losing Eely during two mission scenarios. The goal of this work is to improve Eely’s performance and the likelihood of mission success. Sensitivity analysis results are presented in order to demonstrate the causes having the highest impact on losing Eely.
@inproceedings{sayed2023risk, title = {Risk Assessment of an Autonomous Underwater Snake Robot in Confined Operations}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed}, booktitle = {OCEANS 2023-Limerick}, pages = {1--9}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10244516}, } - Control
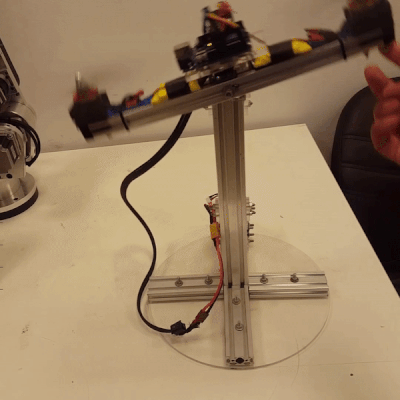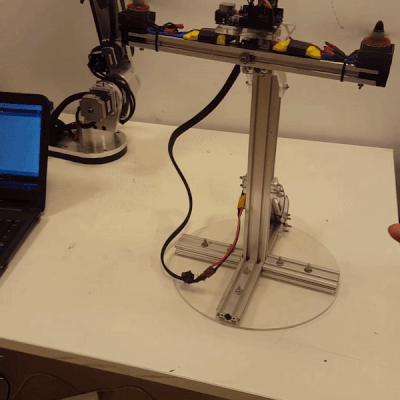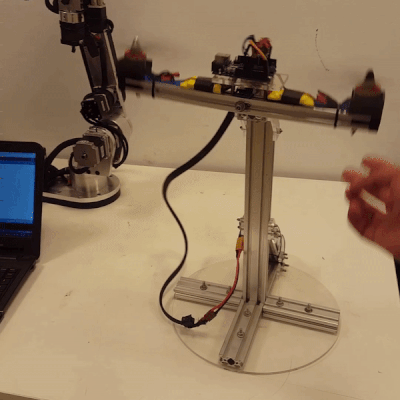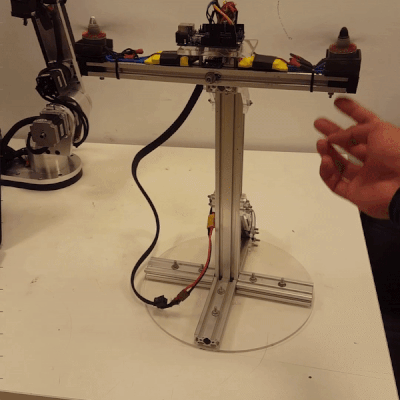 Design of a Fuzzy Type-2 Controller for 1-DOF Pitch Axis Twin Rotor SystemAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Walid K Shaker, Hossam Hassan Ammar, and 2 more authorsIn 2023 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), 2023
Design of a Fuzzy Type-2 Controller for 1-DOF Pitch Axis Twin Rotor SystemAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Walid K Shaker, Hossam Hassan Ammar, and 2 more authorsIn 2023 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), 2023This paper presents the design, manufacturing, modeling, and control of a novel 1-DOF pitch axis Twin Rotor system. An IMU sensor is used to precisely access the desired pitch angle of the system. A type-2 fuzzy controller is designed and implemented to achieve fast rise time and low overshoot, which are the desired response specifications for the system. In terms of overshoot and settling time, the performance of the type-2 fuzzy-PID controller is compared to that of the type-l fuzzy-PID controller and the conventional PID controller. The type-2 fuzzy-PID controller’s performance is promising when compared to that of the other controllers, proving that it is useful for taming the Twin Rotor system’s non-linearities.
@inproceedings{sayed2023design, title = {Design of a Fuzzy Type-2 Controller for 1-DOF Pitch Axis Twin Rotor System}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Shaker, Walid K and Ammar, Hossam Hassan and Azar, Ahmad Taher and Njima, Chakib Ben}, booktitle = {2023 International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD)}, pages = {1--6}, year = {2023}, organization = {IEEE}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10152432}, }
2020
- Robotics
 Centralized multi-agent mobile robots SLAM and navigation for COVID-19 field hospitalsAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Hossam Hassan Ammar, and Rafaat ShalabyIn 2020 2nd Novel intelligent and leading emerging sciences conference (NILES), 2020
Centralized multi-agent mobile robots SLAM and navigation for COVID-19 field hospitalsAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Hossam Hassan Ammar, and Rafaat ShalabyIn 2020 2nd Novel intelligent and leading emerging sciences conference (NILES), 2020In this paper we focus on the proof of concept prototype of fully autonomous centralized Multi-Robot System (MRS) consisting of a Hexapod walking robot and a six wheeled mobile robot. Recently, there has been an increasing demand for such systems as they can be involved in several tasks such as collaborative search and rescue, surveillance, monitoring, and disinfecting Field hospitals. To name a few, COVID-19 pandemic showed the weak points in the medical sector around the world, including those in the most advanced nations that had to go through hard decisions due to the lack of medical supplies and personal protective equipment. The developed system was rapidly adjusted due to COVID-19 pandemic to perform additional tasks like disinfection and remote body temperature detection. The developed system abide by ISO 13482 safety requirements for personal care robots, meaning it will be used and deployed in Field hospitals. We implemented the proposed approach in a game setting of a field hospital where the Hexapod is used to scan and draw a map of the Field hospital environment and to draw a path then the six wheeled mobile robot acts as a medical cargo delivery that enters based on the predefined map and path.
@inproceedings{sayed2020centralized, title = {Centralized multi-agent mobile robots SLAM and navigation for COVID-19 field hospitals}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Ammar, Hossam Hassan and Shalaby, Rafaat}, booktitle = {2020 2nd Novel intelligent and leading emerging sciences conference (NILES)}, pages = {444--449}, year = {2020}, organization = {IEEE}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/9257919}, } - AI & Robotics
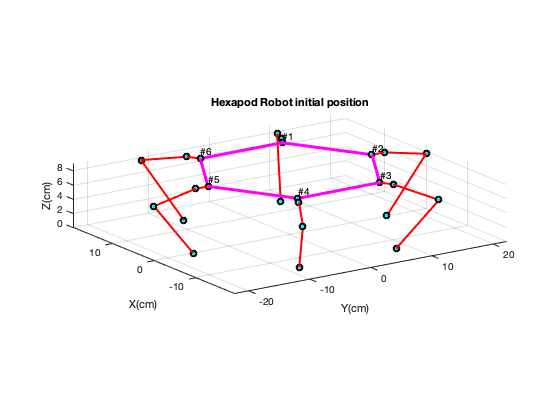 Experimental modeling of hexapod robot using artificial intelligenceAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Amr Ahmed Mohamed, Ahmed Magd Aly, and 4 more authorsIn The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, 2020
Experimental modeling of hexapod robot using artificial intelligenceAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Amr Ahmed Mohamed, Ahmed Magd Aly, and 4 more authorsIn The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, 2020Hexapod Robots gave us the opportunity to study walking robots without facing problems such as stability and expensive custom made hardware. It has a great deal of flexibility in moving over different terrains even if some legs become malfunctioned or facing some difficulties in movement. In this study the kinematic analysis of CH3-R 18DOF Hexapod Robot is discussed where each leg contains three revolute joints in order to mimic the structure of a spider. To develop the overall kinematic model of CH3-R robot, direct and inverse kinematic analyses for each leg have been considered where the Denavit-Hartenberg (D-H) conventions will be used to perform the forward kinematic analysis of the six-legged robot while the inverse kinematics are obtained by simplifying the architecture of the robot into 7 modules, a hexagon trunk and 6 limbs between the trunk and the ground. A neural network (NN) model was employed in order to compare and decide the angles prediction, training time and overall performance with the ones obtained from the analytical solution of the inverse kinematics. The data points used for training the two models and testing their performance was acquired from giving the robot an initial and final position and recording the change in the coordinates and time by using an IMU sensor.
@inproceedings{sayed2020experimental, title = {Experimental modeling of hexapod robot using artificial intelligence}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Mohamed, Amr Ahmed and Aly, Ahmed Magd and Hassan, Youssef Mohamed and Abdulaziz, Abdallah Mahir and Ammar, Hossam Hassan and Shalaby, Rafaat}, booktitle = {The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision}, pages = {26--36}, year = {2020}, organization = {Springer}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-44289-7_3}, } - AI & Robotics
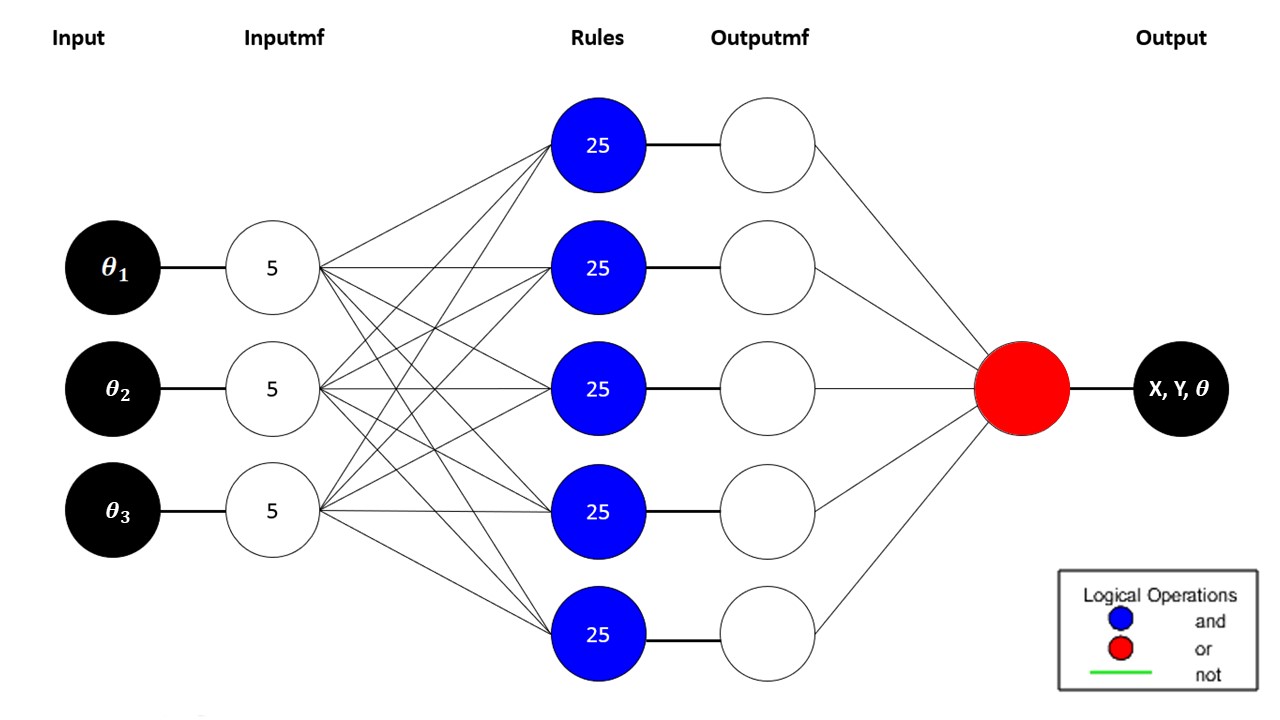 Deep learning based kinematic modeling of 3-RRR parallel manipulatorAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Ahmad Taher Azar, Zahra Fathy Ibrahim, and 3 more authorsIn The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, 2020
Deep learning based kinematic modeling of 3-RRR parallel manipulatorAbdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Ahmad Taher Azar, Zahra Fathy Ibrahim, and 3 more authorsIn The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision, 2020This paper presents a novel low cost design for a 3-RRR Planar Parallel Manipulator (PPM). These manipulators proved their superiority over serial manipulators due to their speed, precision and smaller work space where the work space area is accounted for in the design to ensure that the robot is performing its task in a smooth and simple way without getting into any singularity points. The challenge with PPM is to obtain the kinematic constraint equations of the manipulator due to their complex non-linear behavior. Screw theory is a new approach that is used to compute the direct and inverse kinematics based on the relation between each link and its’ predecessor. The design is then inserted into ADAMS to study its dynamical behavior and to obtain a data set that would be used in analyzing the system in MATLAB. A Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System (NFIS) model was constructed in order to predict the end-effector position inside the work space and it is tuned with Particle swarm optimization (PSO) and Genetic algorithm (GA).
@inproceedings{sayed2020deep, title = {Deep learning based kinematic modeling of 3-RRR parallel manipulator}, author = {Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Azar, Ahmad Taher and Ibrahim, Zahra Fathy and Ibrahim, Habiba A and Mohamed, Nada Ali and Ammar, Hossam Hassan}, booktitle = {The International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Vision}, pages = {308--321}, year = {2020}, organization = {Springer}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-44289-7_29}, }
2019
- AI & Robotics
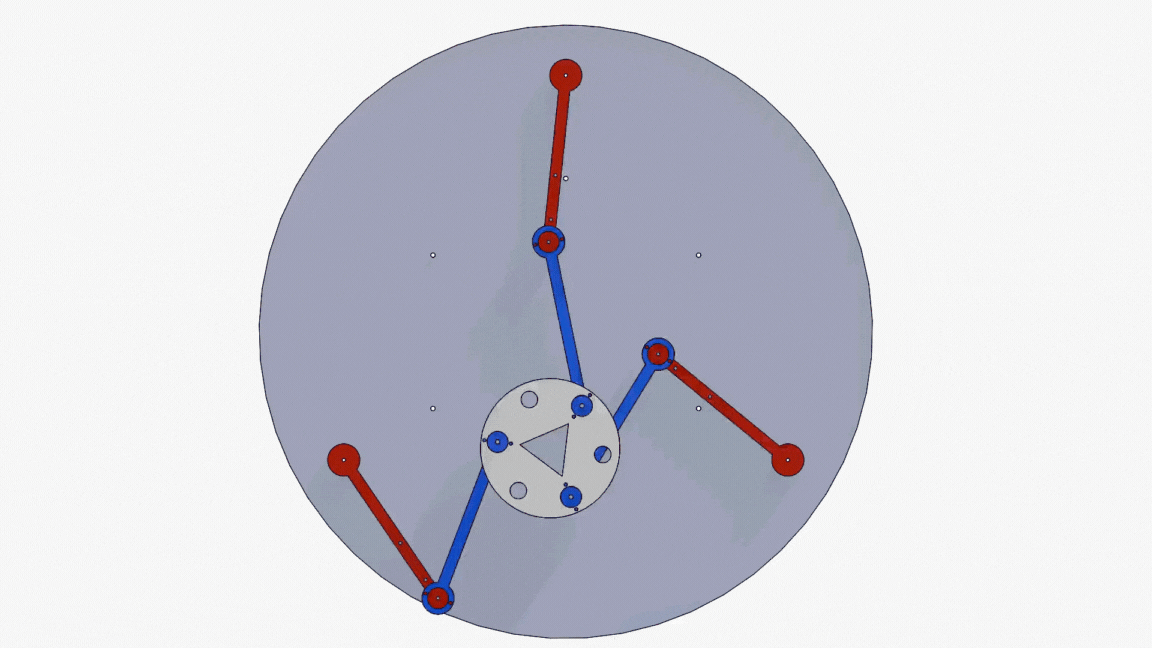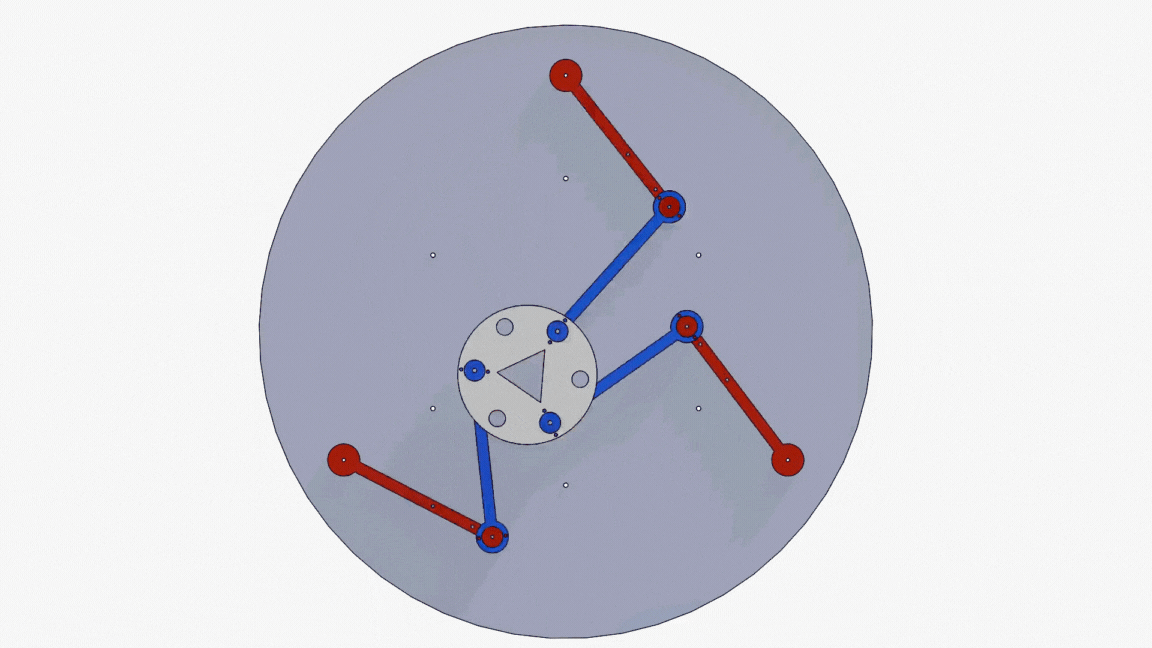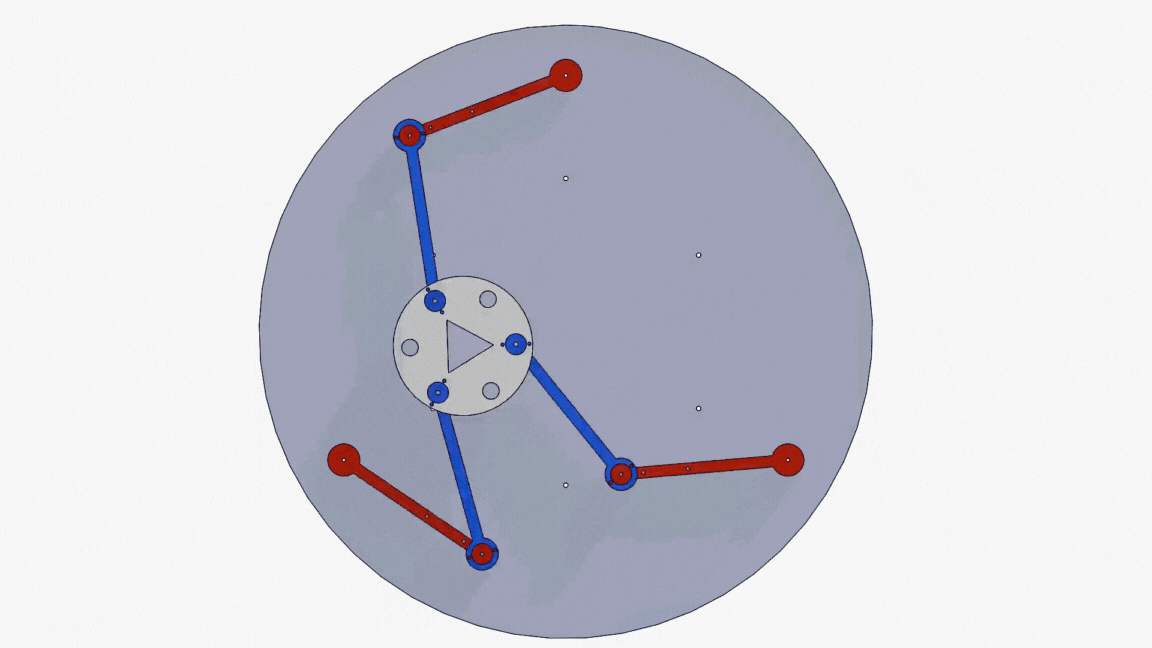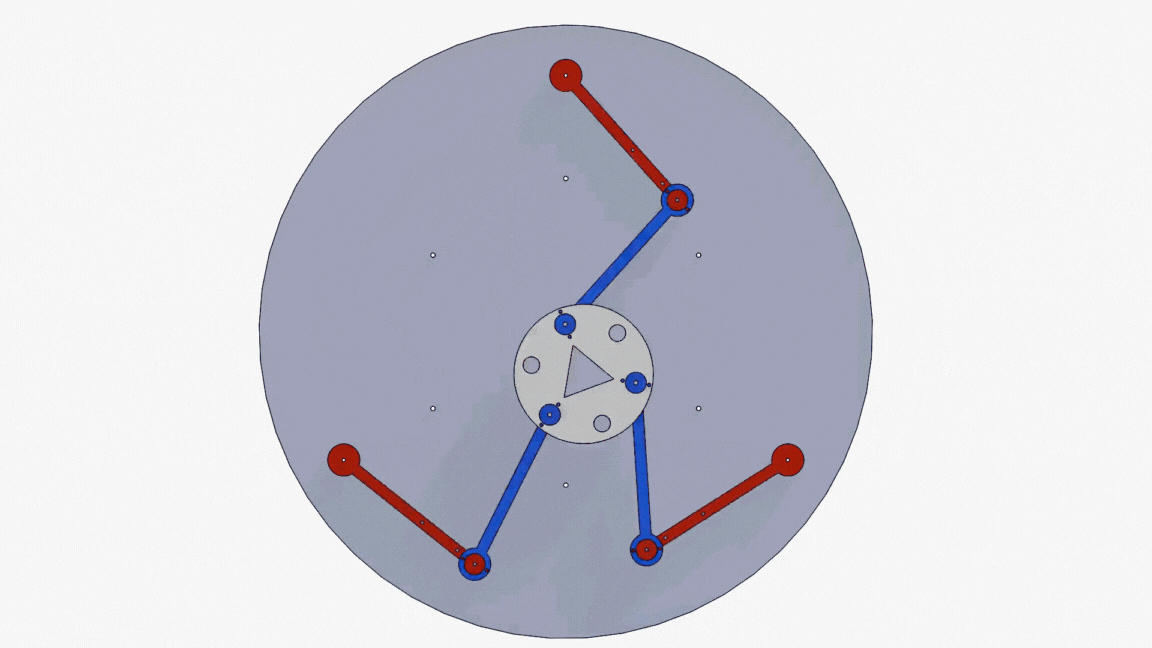 Neuro-fuzzy system for 3-DOF parallel robot manipulatorAhmad Taher Azar, Ahmed Magd Aly, Abdelrahman Sayed Sayed, and 2 more authorsIn 2019 Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES), 2019
Neuro-fuzzy system for 3-DOF parallel robot manipulatorAhmad Taher Azar, Ahmed Magd Aly, Abdelrahman Sayed Sayed, and 2 more authorsIn 2019 Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES), 2019Planar Parallel manipulators (PPMs) are widely used these days, as they have many advantages compared to their serial counterparts. However, their inverse and direct kinematics are hard to obtain, due to the complexity of the manipulators’ behavior. Therefore, this paper provides a comparative analysis for two methods that were used to obtain the inverse kinematics of a 3-RRR manipulator. Instead of the conventional algebraic and graphical methods used for attaining the mathematical models for such manipulators, an adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference structure (AFNIS) model was alternatively employed. It is then compared with a traditional neural network (NN) model for the same manipulator in order to ascertain which model is better in angles prediction, training time and overall performance. The data points used for both training the models and testing their performance are acquired from motion studies in SolidWorks.
@inproceedings{azar2019neuro, title = {Neuro-fuzzy system for 3-DOF parallel robot manipulator}, author = {Azar, Ahmad Taher and Aly, Ahmed Magd and Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Radwan, Mahmoud ElBakry and Ammar, Hossam Hassan}, booktitle = {2019 Novel Intelligent and Leading Emerging Sciences Conference (NILES)}, volume = {1}, pages = {1--5}, year = {2019}, organization = {IEEE}, url = {https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8909333}, } - Control & Robotics
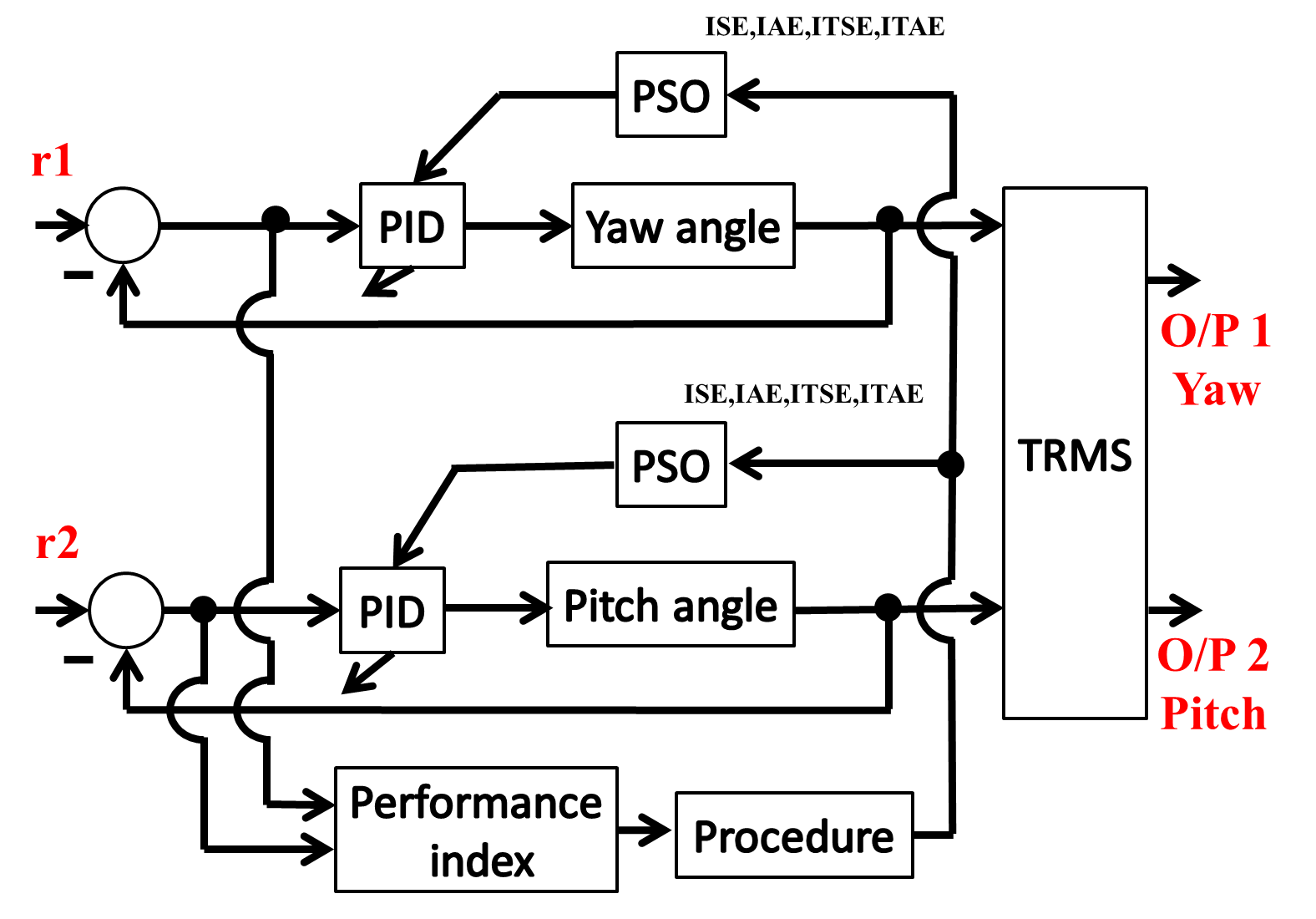 PID controller for 2-DOFs twin rotor MIMO system tuned with particle swarm optimizationAhmad Taher Azar, Abdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Abdalla Saber Shahin, and 2 more authorsIn international conference on advanced intelligent systems and informatics, 2019
PID controller for 2-DOFs twin rotor MIMO system tuned with particle swarm optimizationAhmad Taher Azar, Abdelrahman Sayed Sayed, Abdalla Saber Shahin, and 2 more authorsIn international conference on advanced intelligent systems and informatics, 2019This paper presents the modelling and control of a 2-DOFs Twin rotor multi input multi output (MIMO) system which is a laboratory setup resembling the dynamics of a helicopter. In this paper, the system modelling process is done using the common conventional mathematical model based on Euler-Lagrange method. The transfer functions of the model are used in the different tuning methods to reach the optimal PID gain values. The study uses conventional Proportional-Integral (PI) and Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers to obtain a robust controller for the system. Particle Swarm optimization (PSO) technique was used to tune the controller parameters. A state space model is obtained considering some design assumptions and simplifications. Statistical measurement and convergence analysis is evaluated for the optimization of gain parameters of the PID controller for 2-DOF Twin rotor system using PSO by iteratively minimizing integral of squared error (ISE) and integral of time multiplied by the squared error (ITSE). The results are verified through simulations and experiments.
@inproceedings{azar2019pid, title = {PID controller for 2-DOFs twin rotor MIMO system tuned with particle swarm optimization}, author = {Azar, Ahmad Taher and Sayed, Abdelrahman Sayed and Shahin, Abdalla Saber and Elkholy, Hassan Ashraf and Ammar, Hossam Hassan}, booktitle = {international conference on advanced intelligent systems and informatics}, pages = {229--242}, year = {2019}, organization = {Springer}, url = {https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-31129-2_22}, }